The History and Purpose of the Beaufort Wind Scale
The Beaufort Wind Scale is an empirical measure that relates wind speed to observed conditions at sea or on land. Named after Sir Francis Beaufort, an Irish hydrographer and British Royal Navy officer, the scale has been an essential tool for mariners, meteorologists, and various fields beyond since the early 19th century.
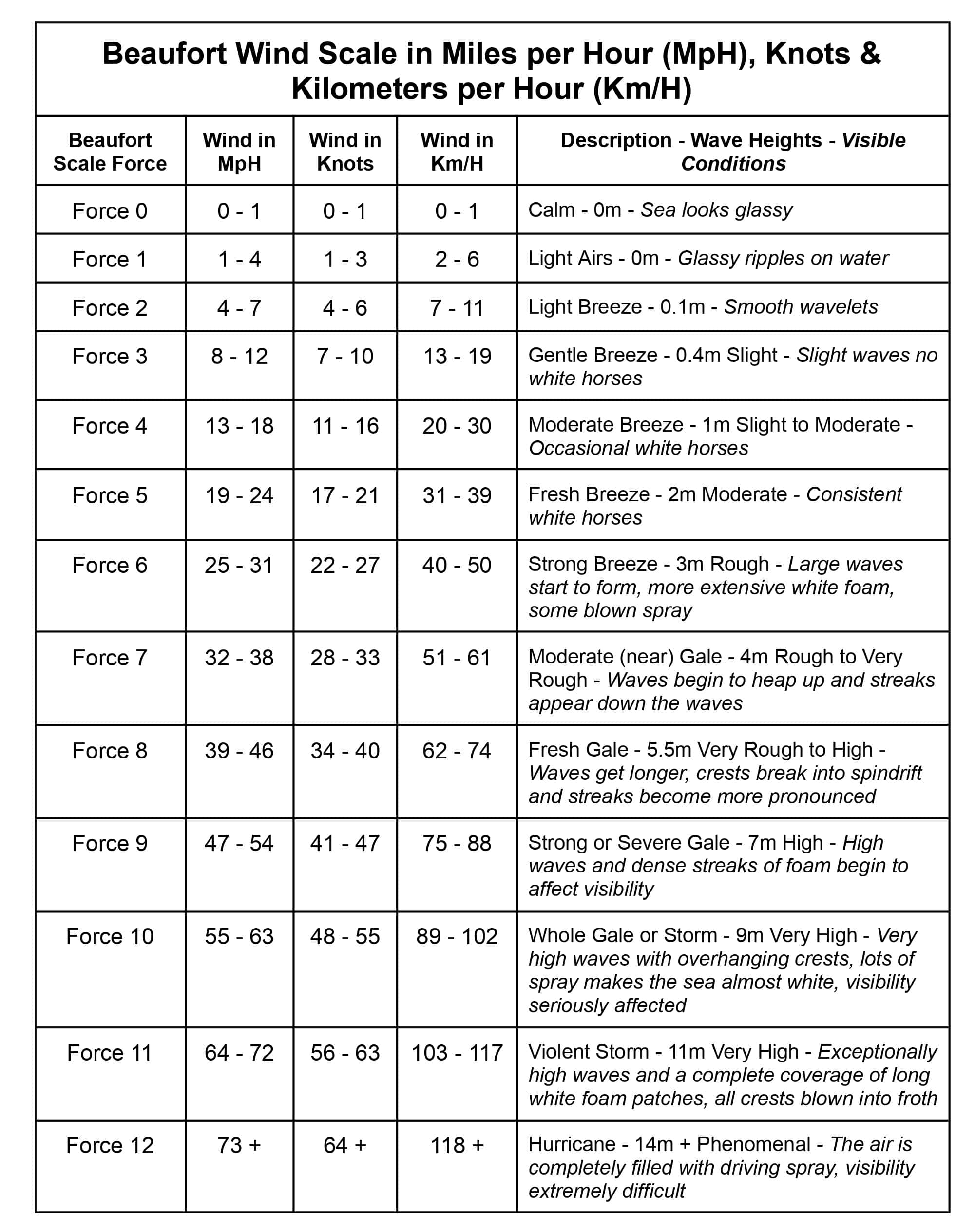
Here it is:
Historical Background
The genesis of the Beaufort Wind Scale dates back to 1805 when Beaufort was serving on HMS Woolwich. He developed a 13-point scale to describe the effect of the wind on the sails of a man-of-war, rather than simply recording the wind speed. This enabled more consistency in the log entries, making them more valuable for navigation and weather forecasting.

Adoption and Standardization
The Beaufort Wind Scale gained official recognition in 1838 when Beaufort became the British Admiralty’s Hydrographer of the Navy. The scale was soon adopted by the Royal Navy and spread to various other nations’ navies.
In 1855, the scale was matched to specific wind speeds in knots, adding an objective element to the otherwise subjective descriptions. The International Meteorological Committee formally extended the scale to land observations in 1916, making it useful for a wider range of applications.
Purpose and Application
Navigation
In the age of sail, the Beaufort Wind Scale provided critical information for sailors to handle their ships appropriately, adjusting sails to various wind conditions.
Meteorology
The scale has proven vital for weather forecasting. By relating wind speed to observable effects on land or sea, it enables more precise predictions and warnings, especially before the advent of modern measuring equipment.
Climate Studies
The Beaufort Wind Scale is also used in climatology, aiding in the study of wind patterns, weather systems, and long-term climate changes.
Summary
The Beaufort Wind Scale, an invention born out of practical necessity, has transcended its original maritime applications to become a global standard for wind measurement. By bridging subjective observation with objective wind speed, it has played a vital role in navigation, weather prediction, and environmental studies for over two centuries. Its lasting impact is a testament to the insight and ingenuity of Sir Francis Beaufort, reflecting an era when exploration and scientific inquiry were closely intertwined.



